Since the September 11th attacks on the United States, many believe that the biggest threat to the United States is from foreign jihadists. Media outlets constantly associate terrorism with foreign jihadist organizations such as ISIL or Al-Qaeda; however, they fail to give adequate attention or coverage to extremist incidents that occur directly on our own soil.
Today, the largest threat facing the United States does not comes from foreign jihadist extremists. Instead, the largest threat to the United States appears to be the rapidly growing threat of domestic violent extremism. Domestic extremism includes homegrown radical Islamist terrorism, right- and left-wing extremism, white supremacist and neo-Nazi extremism, and more. The domestic extremism threat facing our nation today has essentially evolved over time into two major issues that have gone unaddressed by policy makers. First, overseas terrorist organizations have become increasingly adaptable and now use online platforms to recruit vulnerable individuals across the country in order to incite violence. Second, the rise in hate crimes and right-wing extremist events over the past decade has occurred at an alarming rate, and has been disregarded by many public officials and policy makers.
The Recruitment of Jihadi-Motivated Extremists in the US
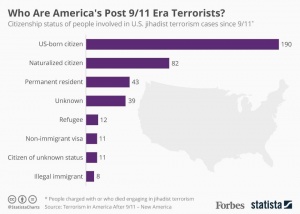
With the availability of new technologies, foreign terrorist organizations no longer need to infiltrate foreign states to attempt attacks of their own. Now, organizations have the capability to recruit, motivate, and initiate attacks online with false messages and propaganda. The rise in Islamophobia has led many to believe that individuals who have conducted such lone-wolf attacks are Muslim or Arab. However, this has not always been the case. According to a study by the RAND Corporation, “the historic stereotype that Muslim, Arab, immigrant males are most vulnerable to extremism is not true to today. Today, recruits in the United States are more likely to be white, black, younger, uneducated, and born citizens.” New America’s study on Terrorism After September 11th explains how since 2001, the number of domestic jihadist terrorism cases
has risen dramatically, from only two individuals being charged in 2001 to a record high of eighty being charged in 2015. The study also reiterates the trend that the majority of the individuals being charged with a lethal extremist attack have been American-born citizens; in fact, according to the study, eighty-five percent of individuals charged with a lethal attack in the United States have been citizens or legal residents. Of this percentage, a majority (two hundred and twenty nine) of terrorism cases have involved American-born citizens. Ninety-nine of the cases have involved naturalized citizens, and fifty-five of the cases have involved permanent residents. Only five cases have involved illegal immigrants, nineteen cases involved refugees or asylum seekers, and twenty-five cases involved non-residents of unknown status. The majority of domestic terrorists are now everyday American citizens and residents who have been inspired by the jihadist movement abroad to take action against the secular West. As Anwar Al-Awlaki, an American-born cleric who joined Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, famously stated, jihad today has become “American as Apple Pie.”
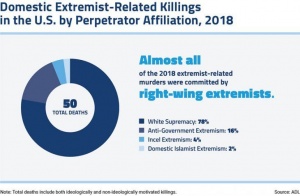
The Rise of Right-Wing Extremism
Jihadi-extremism, while mainly homegrown, now makes up only a small portion of the attacks occurring on American soil. Throughout the last decade, right-wing extremist attacks have risen at an alarming rate. Right-wing extremism includes white supremacy, anti-government extremism, and single-issue movements such as anti-abortion, anti-immigration, and anti-Muslim extremism. While the United States has remained focused on the danger posed by jihadi extremism, there has been a “glaring blind spot” towards the changing dynamic and magnitude of threats facing the United States. According to statistics from the Anti-Defamation League, between 2009 and 2018, 73.3 percent of domestic extremism incidents in the United States were due to right-wing extremism, while only 23.4 percent of incidents were due to jihadist extremism and 3.2 percent were due to left-wing extremism. Furthermore, the rate at which the incidents are increasing is dangerously rapid. In 2018, of the 50 extremist-related murders that occurred, right-wing extremists caused almost all incidents. In fact, right-wing extremists caused 98 percent of the incidents, while only 2 percent of the incidents were caused by domestic Islamic extremism. According to the National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism, individuals targeted for the recruitment of right-wing terrorism are often one of three categories: “frustrated and angry youth looking for solutions to their problems; individuals looking for intimate relationships outside of their families; and younger adolescents who typically lacked maturity and may have been unable to fully comprehend the ramifications of the groups radical ideology.”
Policy Recommendations
- Politicians and policy makers need to make reducing domestic extremism a national security priority.
Domestic extremism needs to be recognized as a major threat. In the past decade, it has largely been ignored and pushed aside by policy makers and politicians, who have been putting a disproportionate amount of attention on the foreign threat of jihadi terrorism. Domestic terrorism needs to be made a federal crime by Congress.
- Seek to increase community awareness about the dangers of all forms of terrorist recruitment, especially in the populations that are deemed to be most vulnerable.
Community awareness programs should partner with the Department of Education in order to educate children, teachers, parents, and guardians about the dangers of terrorist recruitment. The programs should specify the different types of extremism in the United States, the way groups attempt to recruit individuals, and the risks and consequences associated with being involved with such organizations.
- Promote anti-bias intercultural education and after-school programs in elementary and secondary schools.
Education can be the most proactive measure to counter youth radicalization. With the average profile of radicalized individuals being young and uneducated, it is most important to promote educational programs in schools to counter the radicalization and recruitment of young individuals who feel frustrated, angry, and alone. After-school programs should especially be promoted as a way to offer a sense of belonging, community, family, and purpose for individuals who are particularly vulnerable.
- Reframe the Countering-Violent Extremism Program, and reassess how to properly distribute CVE resources.
The CVE program does not just need a new name, it needs to be completely reframed. As of right now, the program has been largely targeted at countering jihadi extremism in the United States, and has cut funding for programs that counter other forms of extremism. Muslim communities have been targeted by the current CVE programs while young black, white and uneducated individuals have become more and more vulnerable to being recruited by different forms of domestic extremism. Funding for grants and research needs to be expanded in order to combat all the different forms of extremism in the United States.
- Make an honest and prioritized effort to countering the ideology of hate.
The United States government must make countering hateful ideologies and extremist groups a top-priority. Politicians have continuously failed to punish right-wing extremist groups for their actions, sending a confusing message about what is constituted as terrorism and when it is considered acceptable to use such violence in the United States. Continuously cutting funding for research grants and for countering right-wing extremism programs has also enabled such issues to escalate in the United States. To stop such incidents from occurring again, changes must be made.






