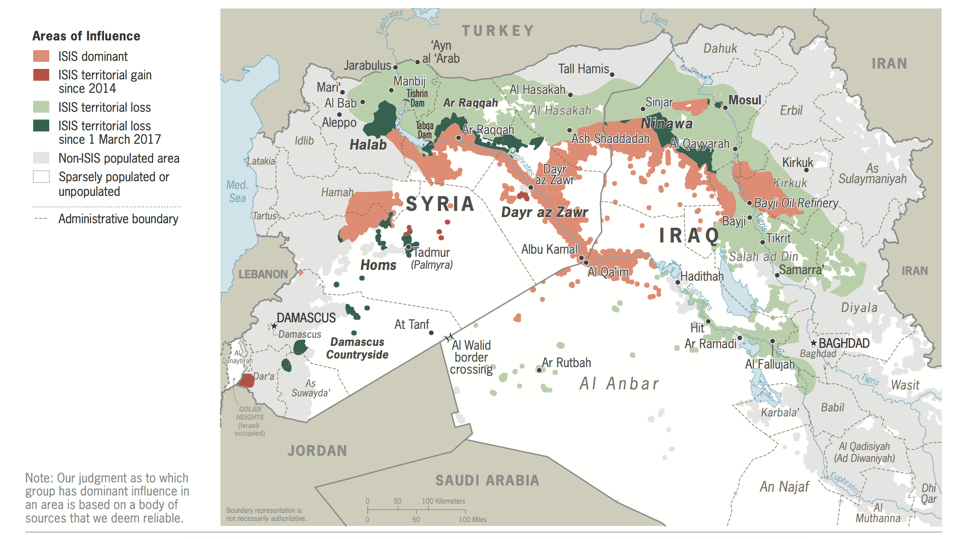
In March, ISIL lost its last physical stronghold in Baghouz, Syria when United States-backed Syrian Democratic Forces overtook the territory. Although ISIL had tangible territory, terrorism is not typically bound by such lines. An examination of how encrypted messaging services, such as Telegram, spread propaganda beyond borders and jurisdictions is required. It is important to comprehend how terror groups and related media sympathizers use such services to influence and recruit.
In a recent case, an ISIL sympathy group, Ash-Shaff, posted propaganda posters on Telegram encouraging attacks in San Francisco, New York City, and London. The posters show images of Big Ben and Parliament on fire, an ISIL fighter running through New York City with an ISIL flag, and a sucidide bomber with a bomb in his backpack. These posters directly target ISIL sympathizers and loan wolves to act. They exhibit messages in English that call for terrorist acts that typically result in a high number of casualties of those deemed kuffar, the expanse of the ISIL network, and targeted countries considered crusaders. Crusaders refers to ISIL adversaries France, Russia, United Kingdom and the United States. The term kuffar is similar to the term infidel.
Ash-Shaff is an ISIL sympathy group either based out of Indonesia or ran by Indonesian citizens. Ash-Shaff creates and shares media to instigate lone-wolf attacks and spread propaganda. They manufactured other pieces of propaganda in January 2019, May 2019, and in July 2019, which were also shared on platforms such as Telegram. All these posters have similar themes, calling out for violence against enemies and trying to incite sympathizers to carry them out. Ash-Shaff is particularly dangerous because sharing content on platforms such as Telegram provide individuals in these channels with the ability to share propaganda on major social media sites.
Ash-Shaff is one of many ISIL supporter media groups. Other major actors include Quraysh Media, Muntasir Media Foundation and Hamlat Fadh Al-Mukhabarat. The list of groups is extensive, but they all serve the same purpose, to share ISIL propaganda. They facilitate communication within ISIL chat rooms on Telegram channels and inspire actions. For instance, during the Sri Lanka bombings, all of the aforementioned groups shared similar propaganda posters and messages on their channels celebrating the attack. What stands out is that a supporter or sympathizer of terrorism does not need to be apart of all these groups to hear the message. Just one is suffice.
Telegram is the top choice to spread terrorist ideas. It is preferred because its messages are fully encrypted and can even self destruct. The company is aware of its appeal to terrorist groups. They have in fact banned ISIL channels from becoming public, but they can remain private. ISIL remains able to use Telegrams private message services to coordinate attacks, plan social media campaigns, and recruit.
One case is telling. In 2017, a woman was arrested in Bandung, Indonesia after she was radicalized in about four months after receiving instructions from over 60 chat rooms on Telegram. It is argued that a radicalized person is ready to perform a terrorist attack in less than a year. An individual who joins five chatrooms can receive up to 500 pieces of propaganda and instruction daily. Telegram chat rooms can host up to 5,000 users.
It is difficult to put a policy solution on encryption services. A solution that has been implemented by Russia and Iran was to ban Telegram altogether. This is not ideal for many countries, but it is effective.
Currently, there are few regulations when it comes to private messaging services. The encryption messaging industry needs to come together and discuss legal and safe parameters. Like the Christchurch Call to Action, main players in encryption services need to develop a platform to combat terrorism. The issue can not be solved by blocking a service, because there is always another one.
The only other solution is that chat rooms exceeding 1,000 users should be charged monetarily. At this level of communication messages are not used for intimate conversations or privacy. Information with such a reach is part of an agenda and meant to spread ideas and information to like minded individuals.
Telegram and other free encrypted messaging platforms are the basis of terrorist communications. They allow for groups to plan social media campaigns, provide instructions for attacks, receive donations and recruit. It is easy to suggest that groups spreading terrorist ideas should be banned from using these services, but it is what needs to be done.