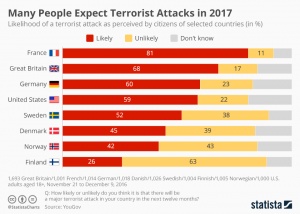
Since 9/11 terror attacks have been presented as an ever-increasing threat in liberal democracies and almost no democratic regime has been immune to these heinous acts. These attacks present a dual menace: both as a genuine threat to the safety of the citizens and, based on the reaction of the government in question, a more insidious risk of undermining the base democratic ideals upon which the state was founded.
French Terror Attacks and State of Emergency Measures
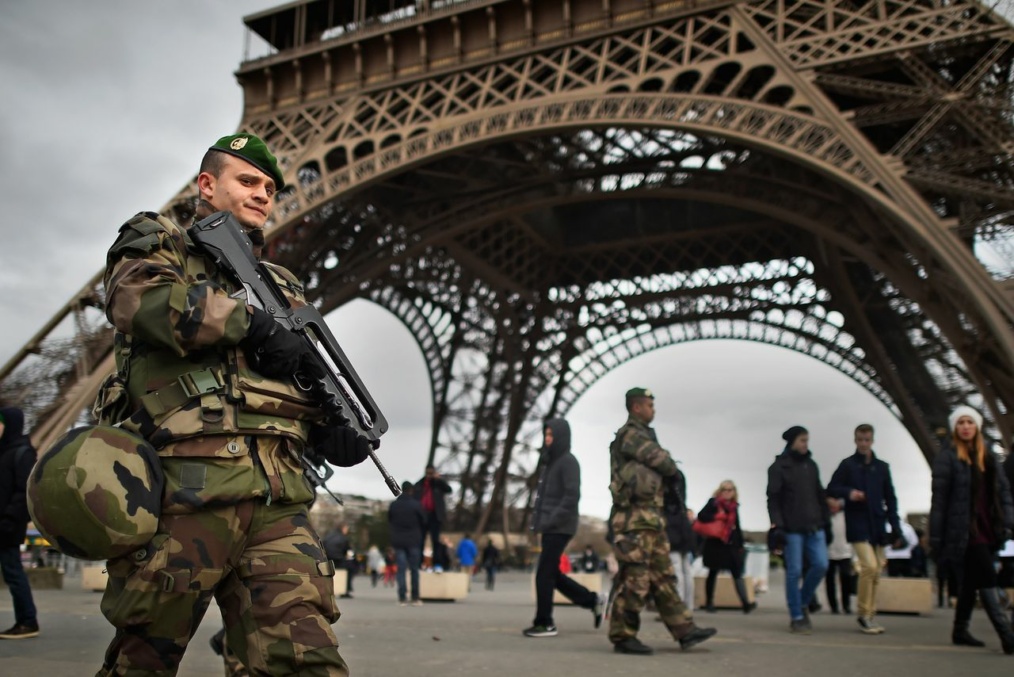
After nearly two decades of relative tranquility, France suffered a string of attacks in 2015 and 2016. Three major attacks hit the country in a short period of time. The offices of Charlie Hebdo, a French political satire magazine, were attacked between January 7th – 9th, and 17 people were killed in shootings both at the office and at a Jewish delicatessen in Paris.
Barely a year later, in November 2015, France again suffered a terrorist attack when a series of coordinated strikes in bars, restaurants, a concert venue and a stadium injured more than 200 people and killed 130.
A few months later, in July 2016, a lone attacker drove a cargo truck through the crowd celebrating Bastille Day on the streets of Nice, injuring more than 400 and killing another 86.
Finally, less than two weeks after the Nice attack, two terrorists attacked a church in Normandy, holding a priest and some of the parishioners hostage. The priest was assassinated, and one parishioner was gravely wounded. The severity of the casualties and the symbolism behind the attacks were unprecedented in France.
Shortly after the coordinated attacks in November 2015, the French government formally declared a “state of emergency,” which had wide reaching impacts on the French government’s executive and legislative powers to quickly curtail any potential terrorist activity. These emergency measures also removed the necessity for prior judicial authorization for police to search houses day or night, and even allowed authorities to impose residence orders, de-facto house arrest, without legislative oversight. In July 2016, these measures were expanded to restrict freedom of assembly and expression, and authorities were expressly permitted to ban public demonstration. Amnesty International described these emergency measures as humiliating and traumatizing to hundreds of citizens.
Slide Towards Civil Liberties Abuses
In light of the extreme nature of the terrorist attacks and widespread public pressure to act, these temporary measures did not initially violate the civil liberties of French citizens. The temporary suspension of some civil liberties, especially with widespread public support, falls within appropriate governmental behavior. However, these powers, once created, did not remain within the stated aim or goal of countering terrorism, but were also applied to inconvenient civilians who posed no legitimate security threat. Protestors of the proposed reforms to labor laws and protestors against COP 21 were both subjected to the same measures as potential radical terrorists.
Emergency powers tend to be like a soft leather glove, they expand to fit the size of the hand wearing them and never again return to the size they were before. In the same fashion, emergency powers tend to expand and grow as they are used, and rarely return to the status quo which existed before they were implemented. The French government, by making some of the draconian emergency measures a permanent part of their legislative framework, has undermined the social contract and has begun to normalize authoritarian-style governance.
It is particularly troubling considering the ambiguity of much of the legal framework of these emergency measures. The unilateral freedom to stop and search, to detain without charge or trial, and to broadly surveil society without a well-defined target beyond the “war on terror” is deeply problematic and opens French society to a myriad of governmental abuses.
Civil liberties have been curtailed and the state of emergency has become entrenched as the new normal. More democratic and legal oversight is needed for such extenuating circumstances. A permanent state of emergency is a paradox used by authoritarian governments as a useful means of social control and the nature of the practice of the security measures in question creates a diminishment of the body of citizenship. Anyone from a migrant background, or Islam, or anyone viewed as being not French enough, became a different class of citizen.
Deradicalization in Civil Society
Any action which silences, marginalizes, or persecutes a particular group in a pre-emptive manner must be resisted by democratic regimes. The insecurity which may accompany this liberty can be addressed with less authoritarian means. France has experimented with softer strategies of de-radicalization; Prime Minister Valls, for instance, pledged to increase the number of moderate imams available in prisons, and that their training would be improved. French prisons tend to be a hotbed of jihadism and working to avoid extremism in the first place is more in line with the responsibilities of a government. It was not, however, a fully-realized measure because, apart from increasing the numbers of prison imams, their status was not elevated or professionalized, a fact that will continue to hamper their overall potential.
France’s admirable effort to introduce moderate imams into the prison chaplain system is an example of a softer attempt to diminish nascent jihadism. Finding a balance between recognizing both the rights and potential threats of Islamic French citizens, while at the same time remaining committed to classic French republican secular values is certainly a difficult task.
It is also imperative that France continually recommits to the protection of civil liberties. A temporary infringement of civil liberties in the face of a crisis is the prerogative, and the absolute duty, of good governance. Proportionality and specificity are of the utmost importance when moving to limit or shape individual freedoms in a democratic society. Creating a permanent state of emergency and using emergency powers, created ostensibly for a single crisis, outside the context in which they were intended is not acceptable in a democratic regime.
Conclusion
It is troubling that France, the birthplace and testing ground of many precious democratic ideals, has taken what can only be described as opportunistic steps towards the violation of civil liberties. If France wishes to remain the citadel of liberty, fraternity, and freedom, it needs to accept a broader plurality of voices contributing to the social contract.
Rather than pathologizing an entire group, and potentially undermining the future civil liberty of other marginalized groups, France should continue its grassroots and societal de-radicalization strategy. This recommitment to an egalitarian society, one which is true to the republican secularism upon which it was founded while giving voice to every citizen, would do credit to the ideals of democracy. The symbol of French liberty, Marianne in her Phrygian cap, losses all meaning if she cannot also be imagined wearing an Islamic headscarf with the same connotations of freedom and fraternity for all.
The biggest challenge presented to the government of France is balancing the long-standing secular republicanism, which has been a cornerstone of French governance since the revolution, against the reality of an ever-growing plurality amongst its constituents, and the genuine threat of terror attacks targeting civilians indiscriminately.
Rory McDonell, Counter-Terrorism Research Fellow