On September 26, a children’s show aired on Iran’s Channel 2 to commemorate the Iran-Iraq war. Translated by The Middle East Media Research Institute, it shows children of different ages dressed in conservative Muslim clothing and military uniforms while praising martyrdom and jihad. In the video, the young protagonists wear badges of Ayatollah Ali Khamenei on their chests and sing a song about their fathers fighting in the Iranian army, willing to die “in the path of God”[1]– presenting a disturbing example of youth indoctrination.
Another recent example of early indoctrination comes from the Indonesian city of Probolinggo, where a kindergarten has been accused of promoting radicalism for dressing children in ISIL-style costumes during an independence day parade.[2]
It is widely known that training is a fundamental component in the strategy of extremist and terrorist groups. The basis for the conservation of the jihadist ideology is to find new proselytes and to plant the seed of hatred in the next generations of jihadis. However, the data reveals this phenomenon to be an increasingly alarming one.
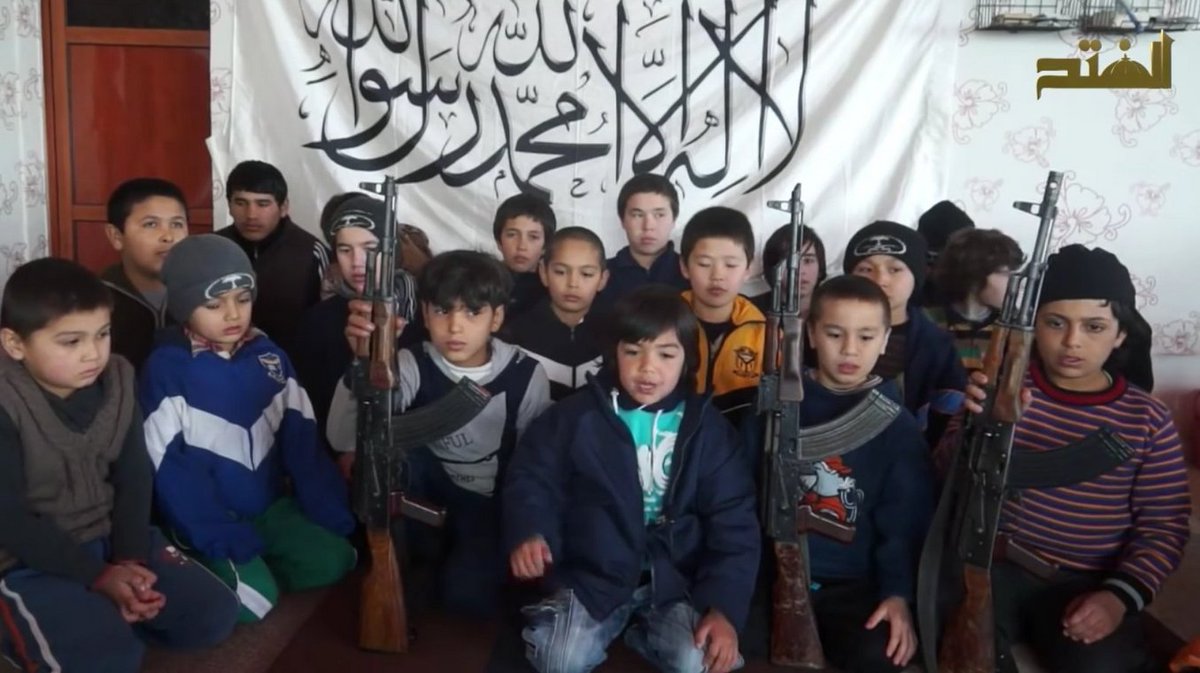
According to a Secretary-General report on children and armed conflict in Nigeria, since 2009 at least 8,000 young soldiers have been recruited by Boko Haram and, by the end of 2016, their army included many boys between 10 and 18.[3] Disconcerting data also suggests that in 2017, the number of recruited children in Somalia (2,127), South Sudan (1,221), the Syrian Arab Republic (961) and Yemen (842) was still remarkably high.[4]

We are all well aware that socio-cultural backgrounds play a leading role in shaping peoples’ future attitudes towards violence, especially in the early years of life. The reason is simple: social groups pass values, customs, beliefs, and rules from one generation to another to ensure a degree of uniformity and the survival of dominant ideologies.
What we often forget is that the transmission of cultural heritage can be both conscious and unconscious, because youth both unintentionally absorb the habits of those around them and deliberately follow instructions given to them by family, schools, peers, and media. This is such an effective means of imparting violent ideology that the innocence of children has now become a matter of grave concern for all of us.
Children are undoubtedly more suggestible than adults; their brains are not yet equipped with knowledge consolidated by past learning processes and experiences. As a consequence, they are extremely receptive to any information which could warp their worldview. The condition of children used as spies and suicide attackers[5] clearly exemplifies the above-mentioned concept: during childhood, critical thinking faculties are underdeveloped, making it difficult for youth to evaluate risks and personally assess the information given to them by jihadis.
Furthermore, jihadi strategists are fully aware of the role emotions play in learning. For this reason, they design specific media content to manipulate children, including songs, cartoons, and games which offer children jihadi role models and spread extremist ideas.
In the face of all this, the outlook seems bleak- so what can we do to prevent children from being drawn to terrorism?
De-radicalization strategies should be targeted at children and primarily based upon human variability because there are different types of extremist movements and the motives involved in joining them vary from person to person. Presumably, no single program could cover them all. In the case of children, we have already discussed how the origins of their radicalization process mainly lies in those people that provide them with role models to identify with. In order to keep children away from violent extremism, it is therefore absolutely necessary to stop adults from supporting or becoming terrorists.
In this digital age, new media has also become a powerful tool for spreading terrorist narratives to children. However, reacting to this threat merely by carrying out cyber attacks or playing the blame game will not help us develop the most effective counter-strategies. To be efficient, any approach should include three main operations: providing an in-depth analysis of terrorist narratives, preparing counter-narratives able to foster intercultural dialogue and mutual understanding, and disseminating counter-narratives (especially through social media and learning institutions.) This will help to reduce the effectiveness of the radical messages children and youth are currently being shown.
Cultural changes require time and cooperation to effectively eradicate dangerous norms and beliefs. But growing the seeds of hope and tolerance will provide our society with a positive foundation for future generations, and it all begins with protecting the youth.
[1] Iranian TV Children’s Show: Standing Next to Missiles, Children Sing in Praise of Jihad and Martyrdom, 9-26-2018, https://www.memri.org/tv/iranian-tv-children-show-children-glorify-fathers-jihad-martyrdom.
[2] Kindergarten dresses children as jihadis for parade in Indonesia, 8-20-2018, https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/aug/20/kindergarten-dresses-children-as-jihadists-for-parade-in-indonesia.
[3] Cf. Report of the Secretary-General on children and armed conflict in Nigeria (S/2017/304), 4-6-2017, p.6, https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/N1709682.pdf
[4] Cf. Report of the Secretary-General on children and armed conflict (A/70/836-S/2016/360), 5-16-2018, p.2, https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/N1815109.pdf
[5] Cf. UNODC, Handbook on children recruited and exploited by terrorist and violent extremist groups, Wien, 2017, p.11, https://www.unodc.org/documents/justice-and-prison-reform/Child-Victims/Handbook_on_Children_Recruited_and_Exploited_by_Terrorist_and_Violent_Extremist_Groups_the_Role_of_the_Justice_System.E.pdf