Author’s note: The Taliban group was founded in the 1990s by Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) and appointed Mullah Omar as founder and Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar as co-founder–the two Pashtun leaders from the Durrani tribe of Afghanistan from heavily populated density provinces in western Afghanistan (Kandahar, Helmand, and Uruzgan regions). In 1996, after the Taliban’s first victory, the Haqqani Network joined the Taliban and since then have committed some of the deadliest bombings and have advanced terrorist targeting capabilities.
A key factor for the prolonged war in Afghanistan has been the thirst for power among the groups and, subsequently, within those groups, other factions, who all want to rule but are unwilling to compromise. There is a layer of interest within each group. The Taliban are a majority-dominated Pashtun-led group that emerged in the 1990s and are now on their second attempt to form their government. However, they are struggling to unify due to tribal, religious, regional, and political differences.
The Taliban took power in Afghanistan in August 2021 but have struggled to maintain power in their second attempt at forming a government. However, the dynamics of the Taliban government have changed.
While the Taliban seeks global recognition, a political dispute between its factions is occurring. Although the Taliban Islamic Emirate is characterized as radical, anti-democracy, and anti-Western values, there are some differences in how Taliban factions view social norms, politics, and governance. The Mullah Baradar Ghani Group is keen to compromise. At the same time, the Haqqani Network is a hard-core extremist group that is unwilling to deviate from its path of an Islamic emirate. The Haqqani Network is considered an extreme faction of the Taliban with no desire to engage with the world, particularly the West.
In general terms, the Haqqani Network, a designated terrorist organization per the U.S. State Department, is considered a more conservative and radical wing of the Taliban. In contrast, Baradar’s group is more liberal and seeks greater rapprochement with the international community.
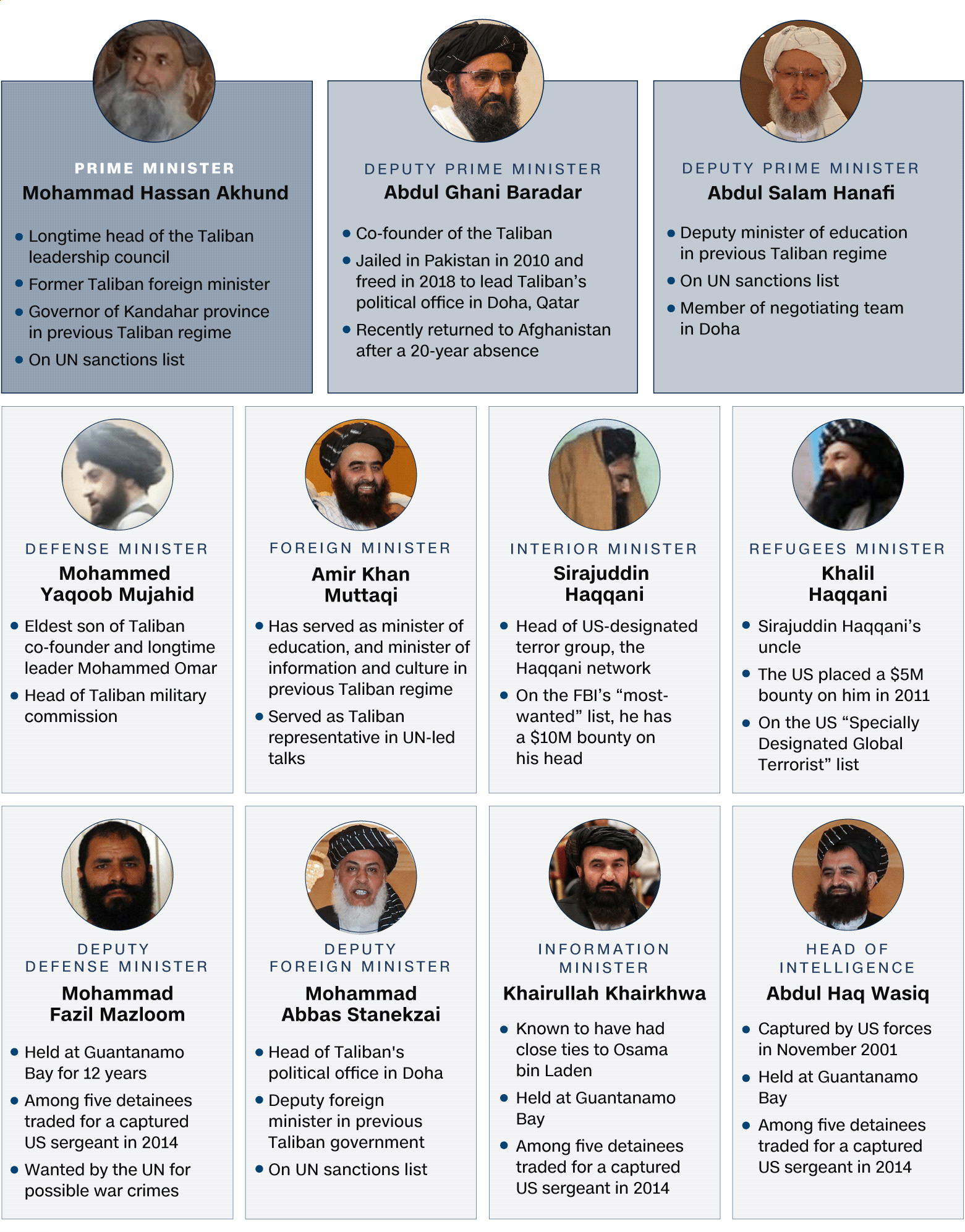
Current Taliban Leadership. Source: The Counter Extremism Project, United Nations, Taliban, Pakistan Foreign Ministry, US Treasury, US State Department Photos: Handout/Taliban, Getty Images, The Counter Extremism Project, US Federal Bureau of Investigation Graphic: Henrik Pettersson, Laura Smith-Spark, Saleem Mehsud, Kara Fox and Tim Lister, CNN
Background
The Haqqani Network was founded by Jalaluddin Haqqani, a Sunni Islamist, and ex-mujahidin warlord during the anti-Soviet war in Afghanistan. During the 80s, Jalaluddin’s group was aided and supported by several members of the international community, becoming one of the most influential groups in Eastern Afghanistan. Furthermore, Jalaluddin had close ties to the Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence and to Osama Bin Laden.
Despite the fact that Jalaluddin died in 2018 from illness, the group continued under the command of his son, Sirajuddin Haqqani.
The Haqqani Network is one of the deadliest terrorist groups in the world. During the Afghan war, they were responsible for some of the highest-profile terrorist attacks against U.S. forces and civilians. For instance, the June 2011 assault on the Kabul Intercontinental Hotel and two major suicide bombings, in 2008 and 2009, against the Indian Embassy in Kabul.
The military and financial power of the Haqqani Network derives from its involvement in illegal activities such as smuggling, kidnapping, and extortion. However, they also receives financial support from agencies such as the Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence and other wealthy donors, which makes the fight against this organization complex.
On the other hand, the Mullah Baradar faction is also seeking political control of Afghanistan. This group seeks to represent the interests of historical Taliban leaders such as Mullah Omar and his son, Mullah Yaqoob, who are originally from the Kandahar region in southern Afghanistan; unlike members of the Haqqani Network, who come from the northeastern region of the country.
Mullah Baradar is the co-founder of the Taliban and participated in negotiations with the United States in Doha during 2020, resulting in the eventual withdrawal of American troops from Afghanistan. Also, Baradar met with Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi in Beijing this year. Mullah Baradar is considered a respected negotiator among the organization and his faction is perceived as the moderate and more liberal wing of the Taliban.
Mullah Baradar’s faction seeks greater rapprochement with the world and is open to negotiation, exemplified by the U.S. negotiations in Qatar. Additionally, this faction proposes a more inclusive government that allows for the participation of ethnic minorities. This approach to foreign policy contradicts the Haqqani Network’s ideals, which, form a more conservative perspective and prefers that other states not interfere in the Taliban government.
The differences between these two factions have led to a current dispute within the Taliban. Mullah Baradar hoped to head the government but instead, he was appointed as a deputy. In fact, on September 21st 2021, there was an armed confrontation between the two groups, resulting in Baradar’s brief disappearance and subsequent move to the Kandahar region.
One of the perpetual afflictions plaguing Afghanistan in the modern era has been an inability for Kabul to consolidate governance over their entire territory. While geography has played a considerable role in this hindrance, it cannot be understated how tribal differences have obstructed the peace process.
In Afghanistan, a significant portion of the Pashtuns are a part of the Durrani confederation and have comprised a large number of the Taliban’s political elite, such as Hamid Karzai. Their power base extends into Pakistan, providing refuge to rebuild strength for future campaigns.
Presently the Durrani are represented by Mullah Baradar, who hopes to continue their monopoly of power within the country. Moreover, with their policy of rapprochement with larger powers, such as China, they can benefit from substantial capital. They could also benefit from arms, which could be used to consolidate power within the country and further transnational infrastructure projects, like the Belt and Road Initiative.
At the moment their primary rivals within Afghanistan are the Haqqani Network, which is primarily composed of the Zadran tribe. The group has traditionally used armed opposition against conflicting foreign powers. Their strength draws from this resistance as well as past alliances with the most dangerous Islamic fundamentalist groups in the region, such as Al Qaeda.
They may see their opposition as only a conduit for foreign influence, and thus feel emboldened to conduct a prolonged conflict against the Duranni faction. Without reconciliation by a third party, the nation may devolve into devastating conflict along tribal and ideological lines, leaving civilians caught in the crossfire.
The most affected: The civilian population
While the Afghan government internally disputes over which Taliban faction should prevail, the civilian population suffers.
Afghans are currently experiencing widespread famine throughout the country. This is due to the current drought, difficult economic climate, and cessation of international food aid.
Today, Afghanistan has a poverty rate of 72%. However, even more worrisome is the notion that the quality of life will continue to decline due to the current political instability, uneconomical public finances, freezing of foreign aid, and the COVID-19 pandemic. If current conditions persist, 97 percent of Afghans could plunge into poverty by mid-2022.
What is next?
The internal dispute between the Haqqani Network and the Mullah Baradar faction is likely to jeopardize the government and consequently negatively impact the civilian population.
Therefore, while the political confrontation between the two factions continues, it is necessary to think about solutions in public policy to prevent and stop the ongoing humanitarian disaster in Afghanistan. It is necessary to evaluate alternatives to intervene on problems such as generalized famine and extreme poverty.
Ahmad Shah Mohibi is the Founder of Rise to Peace and a former US Counter-Terrorism Adviser in Afghanistan @ahmadsmohibi
Christopher Ynclan Jr, Counter-Terrorism Research Fellow
Daniel Ruiz, Counter-Terrorism Research Fellow











