The Mysterious Case of Mohamad Jamal Khweis
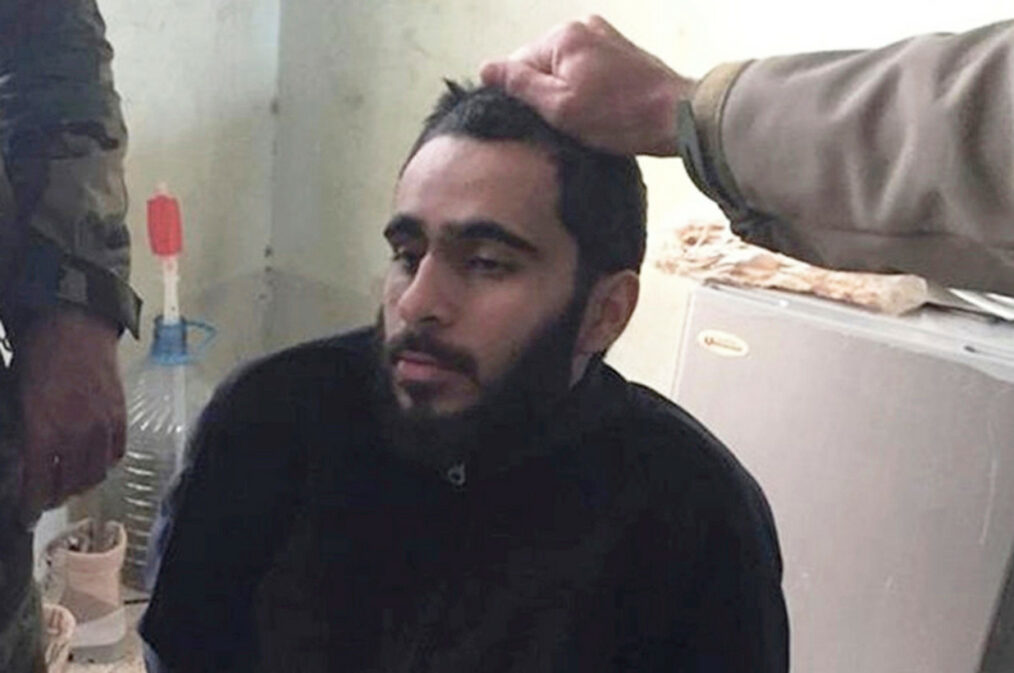
Mohamad Jamal Khweis while in Kurdish custody. Image Credit: Associated Press.
Few in Alexandria, Virginia, would have suspected that the man driving a bus for the elderly would travel halfway across the globe to join the Islamic State (IS) and wage violent jihad. But this is the case of Mohamad Jamal Khweis, who went by the kunya Abu Omar al-Amriki while living in the self-declared caliphate. While the story of Khweis can be compared in some ways to others, not much is known about the actual path of radicalization he took in the lead-up to joining the IS. Khweis consistently lied and changed his story throughout his capture, interrogation, and trial, forcing officials to play a guessing game. What is known about Khweis’ case is analyzed here.
Khweis grew up in the suburbs of Washington, D.C., graduating from Edison High School in Fairfax County in 2007. As the child of two Muslim immigrants from the Middle East, Khweis grew up attending mosque. However, according to his parents, he was not particularly religious growing up. After high school, Khweis got a job as a bus driver for the elderly and disabled. He drank and smoked cigarettes, not activities associated with a devout extremist.
However, something happened between 2007 and 2015. Khweis lied to family and friends in late 2015, a month after the IS attacks in Paris, when he began scheduling travel to Europe. In mid-December Khweis travelled to London before making several stops across Europe en route to Turkey. In Turkey, scheduled contact was made with an IS facilitator who directed him, along with several French would-be jihadists, across the Turkish border and into Syria.
Upon arrival in Raqqa, which was under IS control at the time, Khweis underwent religious training and began work doing miscellaneous household tasks for caliphate fighters. According to documents discovered by forces combating the IS, during this time, Khweis indicated that he was willing to become a martyr by utilizing himself as a suicide bomber for the caliphate.
After months of cooking, cleaning, and taking out the garbage, Khweis grew increasingly frustrated by his lack of military training. Throughout his time in the caliphate, Khweis was also routinely ill from consuming poor-quality drinking water. These factors, and possibly more, combined to make his frustrations unbearable. When Khweis was relocated to IS controlled territory in Tal Afar, Iraq, he made an “escape.”
Kurdish Peshmerga forces discovered Khweis walking alone, and after it was confirmed that he was not a suicide bomber, he was taken into custody. When Khweis was captured he carried several hundred dollars in Iraqi and Turkish currencies, three cell phones, and his Virginia driver’s license. At first, Khweis stated to his captors that he had been deceived by a female he met in Turkey into coming into Syria and essentially becoming a slave; however, this story quickly fell apart. Peshmerga forces were able to contact American authorities to inform them of Khweis’ presence, and he was quickly transferred to American custody. In American custody, Khweis changed his story over 15 times between intelligence interviews and criminal investigation interviews.
Even so, authorities obtained enough information to levy criminal charges. Lawyers representing Khweis argue that this was unfair, and that Khweis gave false information to investigators out of desperation to return to the United States. However, many indicators disprove this- including signs of remaining loyalties, such as Khweis’ refusal to identify or provide any information on Americans he knew who had also joined the IS. Throughout his criminal trial, Khweis again changed his story multiple times, at times even indicating that his time in the caliphate was a mistake made after a night partying in Turkey.
Extremist propaganda was discovered on Khweis’ cell phones after capture, but once again eluding to his own radicalization, Khweis stated that the propaganda was only on his devices because he was conducting research into life in Syria. It is unclear if he was radicalized by online propaganda like so many others. There has not been any mention of other radicalized individuals whom Khweis may have been in contact with in the United States. Ultimately, there is no strong evidence to suggest how Khweis fell towards extremist ideology.
Although a clear path towards radicalization cannot be observed due to Khweis’ lack of cooperation, some comparisons can be made to other cases of radicalization. First, Khweis was the child of Muslim immigrants, growing up in the United States in the wake of 9/11. This time challenged many young Muslims, leading many to seek answers about their identities. It was also a time which caused notable marginalization, or at the very least perceived marginalization, of Muslim communities in the United States.
Circumstantial evidence would suggest that Khweis was vulnerable to radicalization due to his perceived marginalized position in American society. As a child of Muslim immigrants in post-9/11 America, Khweis certainly grew up with various forces pressuring him and challenging his identity. While not much more can be properly guessed about what exactly occurred along Khweis’ journey, his uncooperative nature and refusal to provide information about other American jihadists belies the fact that he likely remains radicalized. Fortunately, his 20-year sentence for providing material support to the IS will provide critical time that may lead to more cooperation and insight into his beliefs and radicalization process.
John Patrick Wilson is a Law Enforcement Professional and Research Fellow for Rise to Peace.



