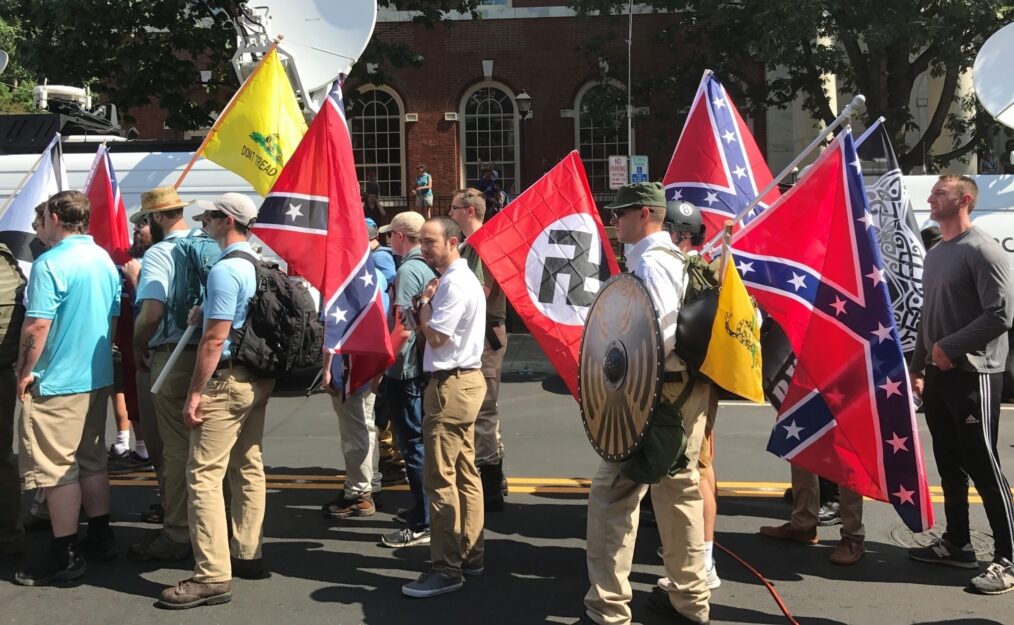
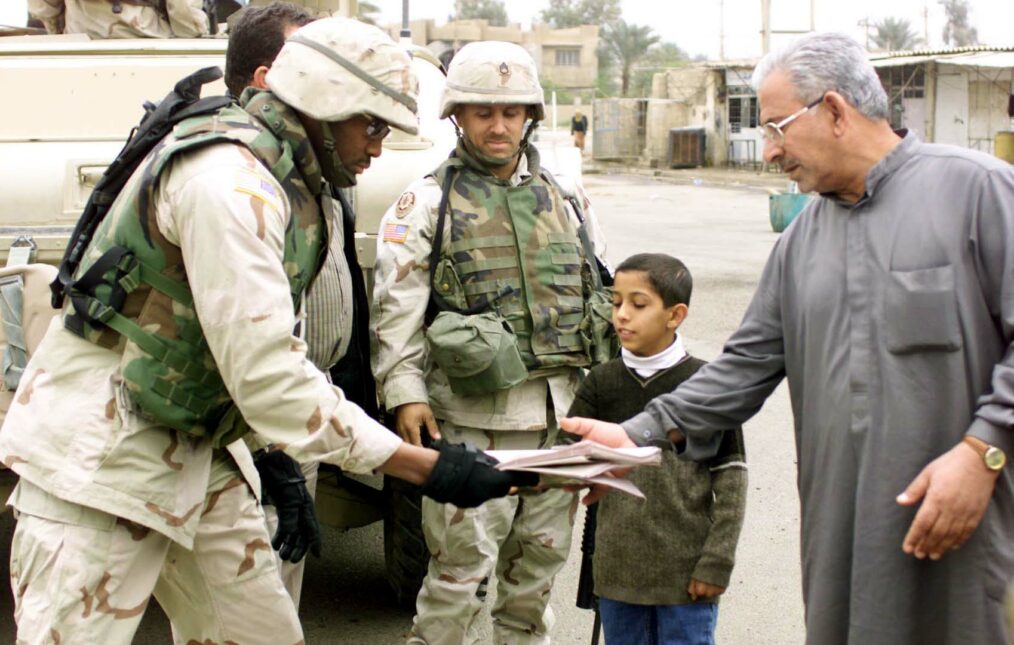
Far-right protestors at the “Unite the Right” rally in Charlottesville, Virginia, August 2017. Image credit: Anthony Crider.
In the United States, many would argue that one of the greatest threats to national security is terrorism, but its portrayal in media and politics has convinced most Americans that the threat only comes in the form of Islamic extremism. However, the threat of terrorism is diversifying. The number of domestic terrorists in the U.S. exhibiting ideological tendencies associated with right-wing extremism is increasing. Most recently, Robert Bowers killed eleven Jewish worshippers at the Tree of Life Synagogue in Squirrel Hill, Pennsylvania on October 27, 2018. He faces 29 criminal charges and potentially the death penalty. Some have profiled the incident as the largest attack on the Jewish Community in the history of the United States- but Mr. Bowers is not the only extremist to engage in such activity as of late. Cesar Sayoc Jr., who this autumn mailed explosive devices to Hillary Clinton, George Soros, former president Barack Obama, and other prominent Democratic figures, was arrested in Florida and faces five federal criminal charges, including interstate transportation of an explosive, illegal mailing of explosives, making threats against former presidents, and assaulting federal officers.
Incidents such as these are increasingly common. In 2017, there were a total of 65 domestic terrorism incidents in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of these incidents involved individuals who exhibited anti-Semitic, racist, xenophobic, homophobic, anti-government, or fascist motivations. The remainder of the attacks were driven by left-wing ideologies and Islamic extremism. To give further context, the number of global terrorism incidents saw a decline of almost 40 percent, going from about 17,000 attacks in 2014 to about 11,000 attacks in 2017. Meanwhile, incidents in the United States increased nearly 10% from 2016 to 2017. Even as the total number of global terrorism incidents has seen a great decline, the United States itself has seen a significant increase in domestic terrorism. Given the complex profiles of recent domestic terrorists, it may be difficult to pinpoint the reasoning behind why exactly they carry out the attacks. However, such analysis is critical, as it can help us learn to identify and thwart future attackers.
The rise in domestic terrorism, and specifically right-wing extremism, stems from multivarious motivations. Some attackers exhibited warning signs, such as suspicious social media activity; both Robert Bowers and Cesar Sayoc vented their frustrations on the Internet before carrying out acts of terrorism. For others, such as the Las Vegas shooter Stephen Paddock, who killed 59 people, the motivation was unclear and has yet to be discovered. The cases of Bowers and Sayoc clearly prove that social media companies are not doing enough to monitor their users’ content and alert authorities to potentially dangerous individuals who may pose a threat to society. Platforms such as Gab, the social media website that Bowers used to post anti-Semitic videos and other content, has a user base of nearly 800,000 people, many of whom politically identify as members of the far-right (Molina, 2018). Many of these individuals have been removed from other social media platforms for posting hate speech and other forms of obscenity in the past. After the incident at the Tree of Life Synagogue, Gab went offline and suspended numerous user accounts. Gab’s service provider, GoDaddy, found that Gab had violated its terms of service by allowing the content that encouraged and promoted the use of violence, and subsequently gave Gab 24 hours to find new service provider to host the website.
The case of Gab reveals many reasons as to why Bowers was not identified as a threat or referred to law enforcement. First, his posts were not identified as “threatening” by platform regulators. Second, his posts were not taken down, despite their clear containment of threatening speech. Third, Gab did not inform or collaborate with law enforcement authorities to alert them that Bowers could be a threat to society. However, Gab is not the only platform guilty of this. Sayoc also had exhibited significant social media usage before carrying out the attempted mail bombings. He had used Twitter months before, sending threatening tweets to George Soros and former Attorney General Eric Holder. Clearly, these cases highlight the need for social media platforms to adapt their current regulation of user content, as well as their collaboration with U.S. law enforcement. There seems to be a pattern with many domestic terrorists in using social media as a platform to vent their grievances. By identifying these grievances in a timely manner, countless lives may be saved.